API Request Lifecycle
To understand how requests are processed in Dominion framework lets look on their lifecycle, it’s straight forward:
-
On startup framework goes through all registered controllers, generates URI based on functions interface and make mappings between URI’s and those functions.
-
Client makes request to API server.
-
Framework’s router catches a request and looking for matching endpoints from ones registered in controllers.
-
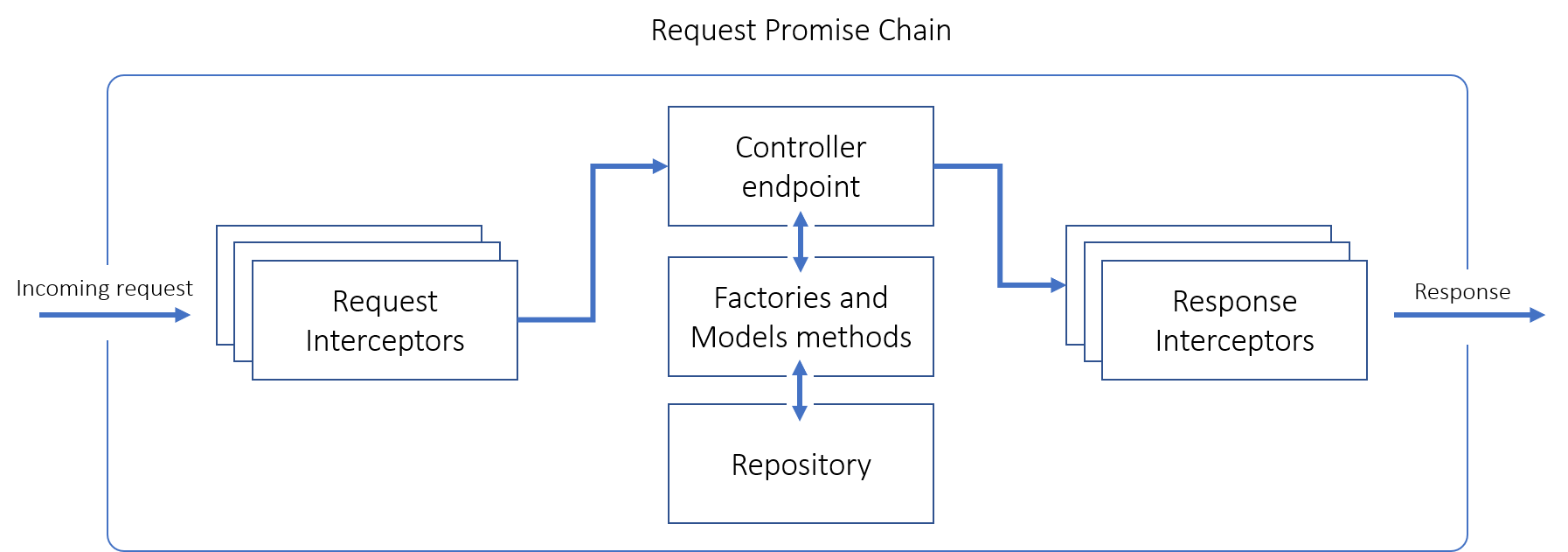
If match was found, router builds request Promise chain. This means that all functions in a chain will receive as an argument execution result of previous function or Promise resolution returned by previous function. Also, if any of the function throws an exception all consequent functions will not be executed, unless there will be
.catch()with manual exception handling.
A chain contains request interceptors, endpoint function (function defined in a controller), response interceptors and request finalisation. Afterwards, request promise chain gets executed.- Requests interceptors are taking from
requestInterceptorsarray in component’s declaration file. They are general purpose functions that may validate client’s authorization. - Then
endpointgets executed. It defines top level business logic. Usually controller’sendpointsmanipulates models created byFactories. If needed, factories or model instances call linkedRepositoryto create/modify/remove data in DB or other permanent storage.endpointmay return Promise, serializable Object or primitive. - Result of
endpointexecution is passed to response interceptors. They are taking fromresponseInterceptorsarray in component’s declaration file. There are no common use for response interceptor, asendpointis responsible to produce response that is ready to be send back to client. However, it may be used to perform some general actions that depends onendpoint's response, like set custom header. - Lastly, router handles common exceptions produced by
endpoint,FactoriesorRepositoy. If any, it will set proper status code (400 - for bad request, 404 - if model not found, 409 - for conflicts, etc).
- Requests interceptors are taking from
-
After it’s done, response produced by all previous steps gets stringified and returned to a client.